Eintritt Gratis, Alter: 16-25 Jahren
Wellen – Tauch ein!
focusTerra, das Earth & Science Discovery Center der ETH Zürich, nimmt dich mit auf eine spannende Reise aus dem Inneren der Erde, vorbei an den Gipfeln der Alpen bis hoch hinaus zu den Sternen. In der Sonderausstellung «Wellen – Tauch ein!» kannst du mit vielen interaktiven Experimenten spielerisch und mit allen Sinnen die Bedeutung, Schönheit und Kraft von Wellen entdecken.
Handy-Anruf: gefährlich oder harmlos?
Wenn du einen Anruf tätigst, sendet und empfängt dein Handy elektromagnetische Wellen im Mikrowellenbereich. Einige dieser Wellen werden von deinem Körper aufgenommen. Miss mit deinem eigenen Handy, wie stark du den Mikrowellen ausgesetzt bist! Mark G. Douglas, der Projektleiter von IT is Foundation, ist Experte auf dem Gebiet der Elektromagnetik und beantwortet deine Fragen.
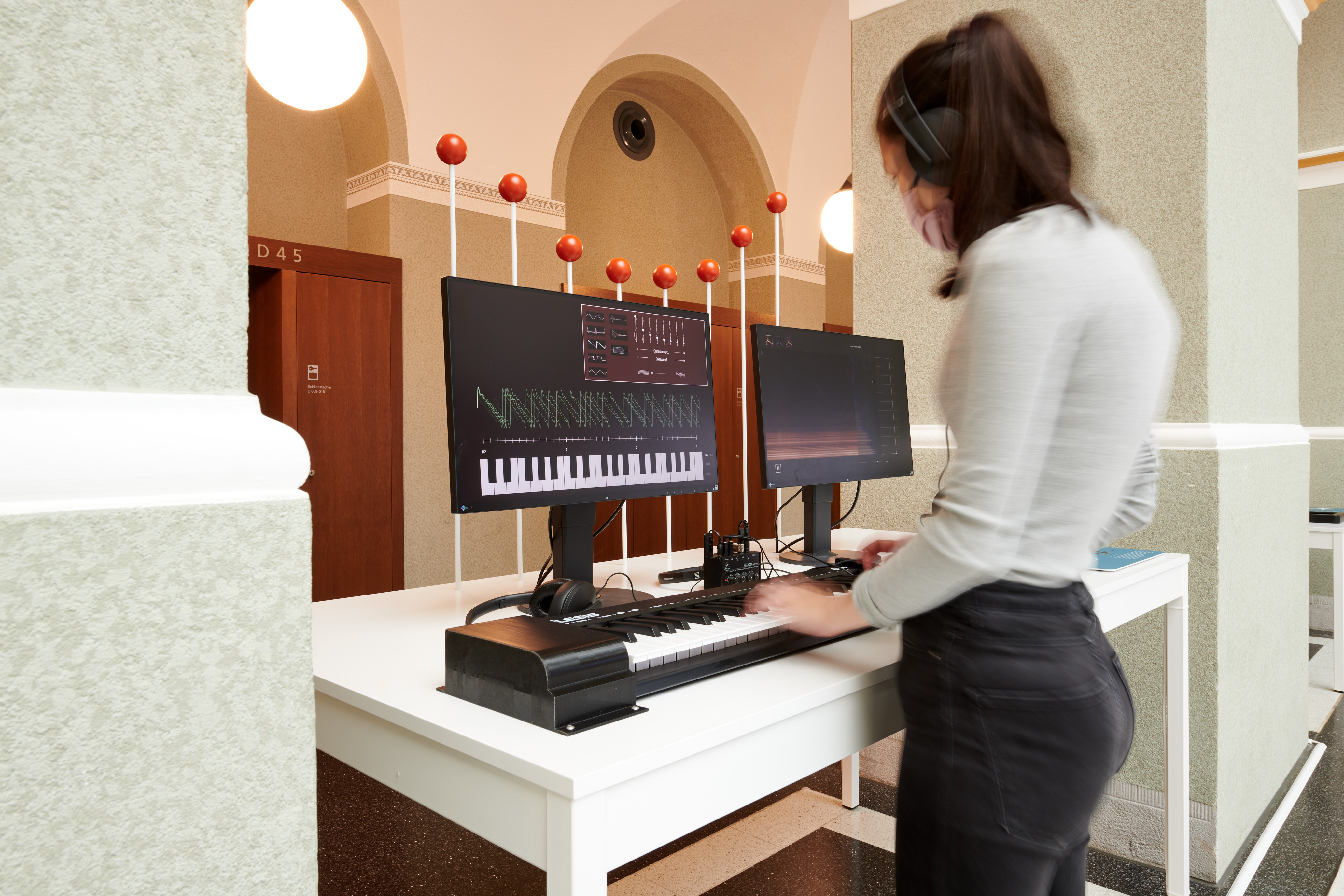
Mach Musik und analysiere die Klänge
Zwei verschiedene Instrumente klingen unterschiedlich, auch wenn auf ihnen der gleiche Ton gespielt wird. Woran liegt das? Finde es heraus!
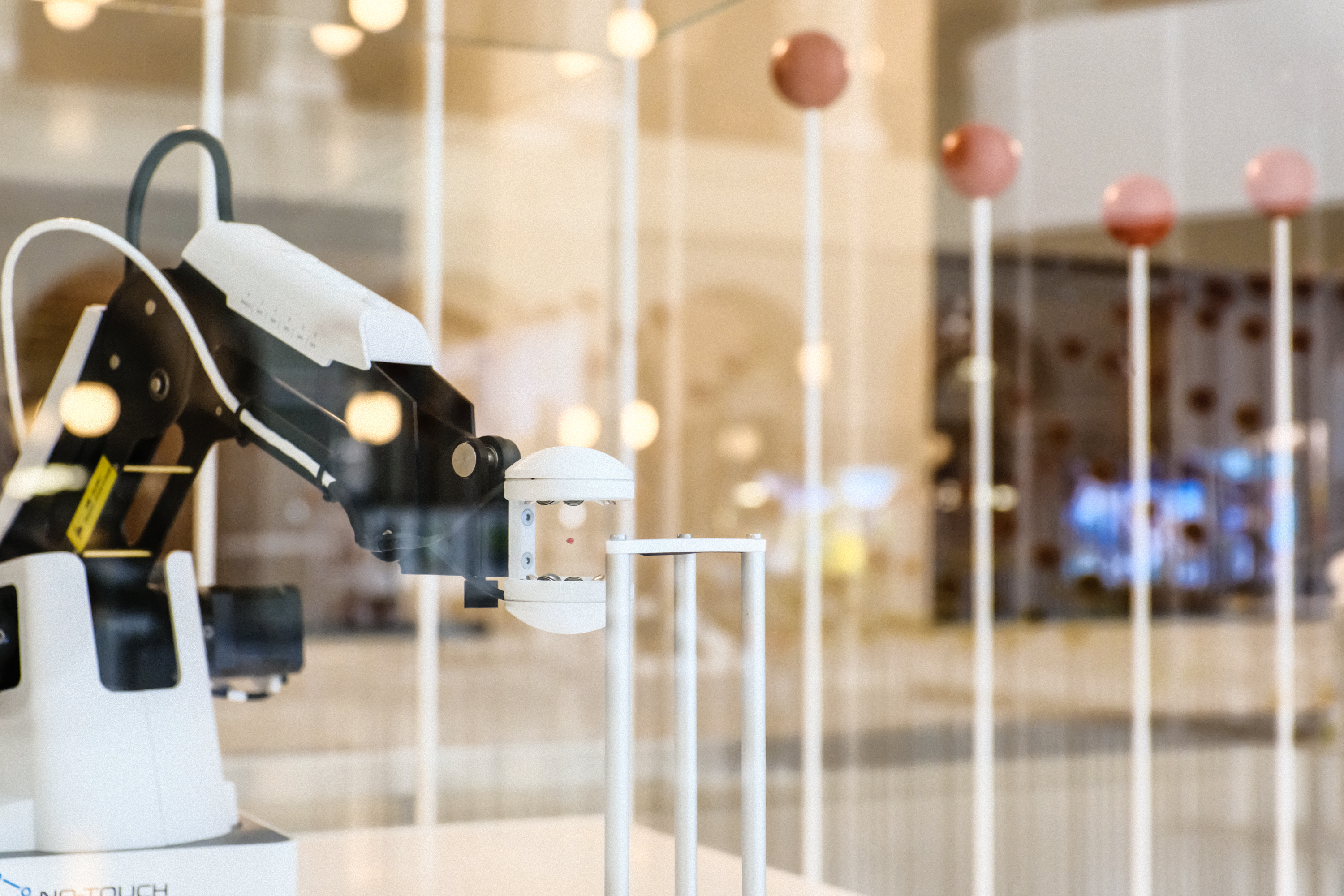
Lass ein kleines Objekt schweben
Fast wie Magie: Der vom ETH Start-up entwickelte Robotergreifarm kann Objekte greifen, ohne sie zu berühren – nur mithilfe von Ultraschallwellen. Diese entstehen, wenn viele kleine Lautsprecher ein akustisches Druckfeld im nicht hörbaren Bereich erzeugen. Mehr darüber erfährst du vom Gründer Marcel Schuck, CEO, No-Touch Robotics.
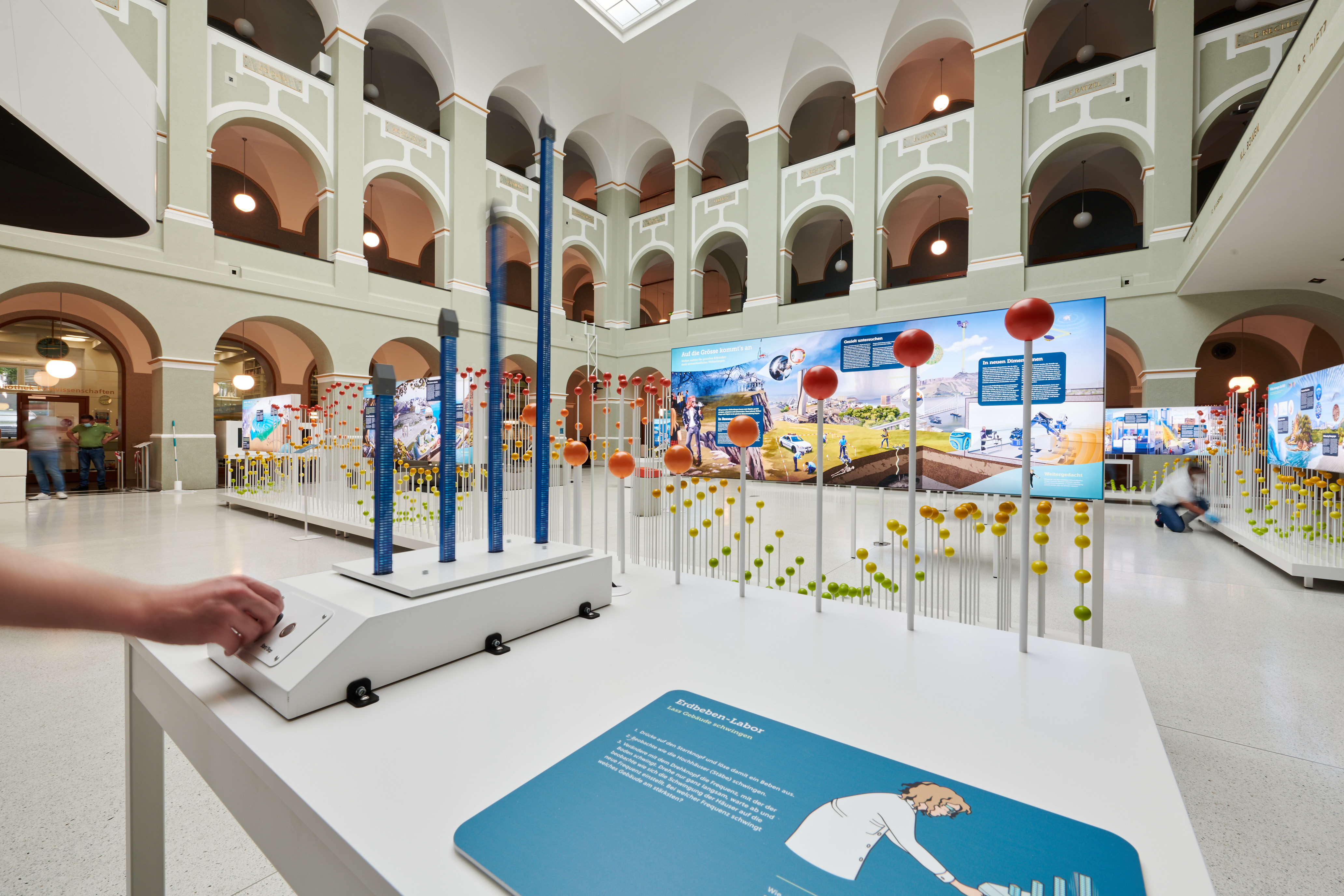
Spüre, wie sich ein Beben anfühlt
Wieso bebt die Erde und wo? Wie fühlt sich ein Erdbeben an? Wie kann ich mich schützen? Bei einem Besuch im Erdbebensimulator kannst du all dies erfahren – und ein echtes Erdbeben am eigenen Körper erleben.
Mach Wellen!
Im Wellenkanal Wavenator 3000 kannst du mit diversen Strand- und Riff-Bausteinen testen wie Wellen brechen. Auch virtuell kannst du deine eigenen Fotos als 3D Objekt in die Strömung legen und beobachten, wie dein Bild virtuell Wellen schlägt. Experimentiere mit Lisa und Mauro vom Team SPINNat, dem Thinklab für kreative SPINNereien der ZHdK.
Gegen den Strom Schwimmen
Ultraschall kann als Energiequelle genutzt werden, um kleinste Teilchen mikrometer genau zu platzieren. Schallwellen gelten bei hohen Frequenzen als sicher, nicht invasiv und kostengünstig. Dies führt zu nützlichen Anwendungen in der Biomedizintechnik Diagnostik und Medizin, wie z.B. das Einsetzen von Stents oder das Navigieren von Medikamenten an schwer zu erreichende Stellen.
Prajwal Agrawal, Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiterin ARSL lab, ETH
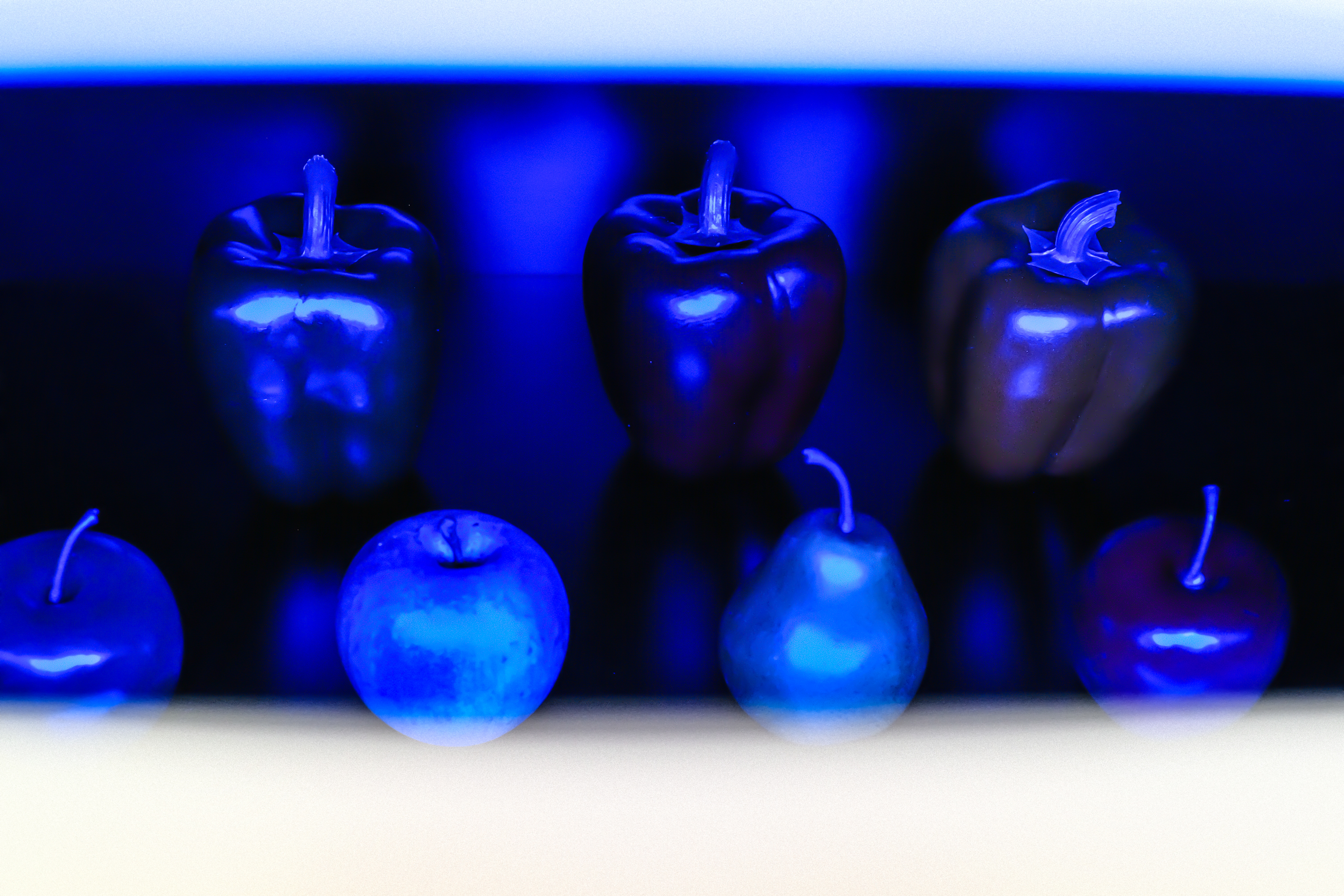
Erkenne Objekte in verschiedenen Farben
Wir Menschen sehen die Welt normalerweise in weissem Licht – das aus allen Farben des Regenbogens besteht. Betrachten wir einen roten Apfel, erscheint er rot, weil er den roten Lichtanteil reflektiert und alle anderen Farbanteile «verschluckt». Doch welche Farbe hat der Apfel, wenn er von rein grünem, rotem oder blauem Licht angeleuchtet wird? Gelingt es dir, den roten vom grünen Apfel zu unterscheiden?
Lass Gebäude schwingen
Wie der Boden bei einem Erdbeben schwingt, hängt von der Art des Bebens und der Beschaffenheit des Bodens ab. Die Schwingung des Bodens überträgt sich auf die Häuser, wobei es für jedes Haus eine bestimmte Frequenz gibt, bei der es maximal schwingt – die Resonanzfrequenz. Die Kenntnis von Bodenschwingungen und Gebäude-Resonanzfrequenzen ermöglicht erdbebengerechtes Bauen. Finde heraus, welches Gebäude bei welcher Frequenz in Resonanz schwingt!
DJ Duo SOLE
Musik legt an diesem Abend DJ Duo SOLE auf. Musik Genre: Electro Techno World.
#helvetiarockt
Bilder:
Foto «Erdbebensimulator»: Peter Rüegg, HK
Foto «Greifarm und Farbkasten»: Astrid Robertsson
Foto «Erdbebenlabor und Tonstudio»: Matthias Auer
Admission free, Age:16-25
Waves - Dive in!
focusTerra, the Earth & Science Discovery Center of ETH Zurich, takes you on an exciting journey from inside Earth, past the peaks of the Alps to high up in the stars. In the special exhibition ‘Waves - Dive in!’ you can discover the meaning, beauty and power of waves with all your senses and with lots of interactive, playful experiments.
Cell phone calls: dangerous or harmless?
When you make a call, your cell phone sends and receives electromagnetic waves in the microwave range. Some of these waves are absorbed by your body. Use your own cell phone to measure how exposed you are to microwaves! Mark G. Douglas, the project director of IT’IS Foundation, is an expert in the field of electromagnetics and will answer your questions.
Make music and analyze the sounds
Two different instruments sound different even when the same tone is played on them. What is the reason for this? Find out!
Make a small object float
Almost like magic: the robot gripper developed by the ETH start-up can grasp objects without touching them – by means of ultrasonic waves. These are created when small loudspeakers generate an acoustic pressure field in the inaudible range. Find out more from founder Marcel Schuck, CEO of No-Touch Robotics.
Feel the quake
Why is Earth shaking and where? What does an earthquake feel like? How can I protect myself? Learn about all this – and experience a real earthquake during a visit to the earthquake simulator.
Make waves!
You can test how waves break with various beach and reef building blocks in the wave laboratory Wavenator 3000. You can also virtually place your own photos as 3D objects in the current and watch how your picture virtually creates waves. Experiment with Lisa and Mauro from Team SPINNat, a ZHdK thinklab for creative, crazy experiments.
Swimming upstream on sound waves
A sound wave can be used as external energy to place tiny particles with precision in mirometers. At high frequencies, sound waves are considered safe, non-invasive and relatively inexpensive. As a result, this leads to useful applications in biomedical engineering diagnostics and medicine, such as inserting stents or navigating drugs to hard-to-reach locations.
Prajwal Agrawal, Research Associate ARSL lab, ETH
Recognise objects in different colors
We humans normally see the world in white light – which consists of all the colors of the rainbow. If we look at a red apple, it appears red because it reflects the red part of the light and ‘swallows’ all other color parts. But what color is the apple when it is illuminated by pure green, red or blue light? Can you distinguish the red from the green apple?
Make buildings swing
How the ground vibrates during an earthquake depends on the type of earthquake and the nature of the ground. The vibration of the ground is transmitted to the buildings and for each building there is a specific frequency at which it vibrates at its maximum – the resonance frequency. Knowing soil vibration and resonance frequencies of buildings allows for earthquake-resistant construction. Find out which building resonates at which frequency!
DJ Duo SOLE
DJ Duo SOLE will play music this evening. Music Genre: Electro Techno World. #helvetiarockt
Images: Photo ‘Earthquake simulator’: Peter Rüegg, HK; Photo ‘Gripper arm and paint box’: Astrid Robertsson; Photo ‘Earthquake lab and recording studio’: Matthias Auer